Understanding the peer review process
What is peer review? A guide for authors
The peer review process starts once you have submitted your paper to a journal.
After submission, your paper will be sent for assessment by independent experts in your field. The reviewers are asked to judge the validity, significance, and originality of your work.
Below we expand on what peer review is, and how it works.

Peer review is the independent assessment of your research paper by experts in your field. The purpose of peer review is to evaluate the paper’s quality and suitability for publication.
As well as peer review acting as a form of quality control for academic journals, it is a very useful source of feedback for you. The feedback can be used to improve your paper before it is published.
So at its best, peer review is a collaborative process, where authors engage in a dialogue with peers in their field, and receive constructive support to advance their work.
Use our free guide to discover how you can get the most out of the peer review process.
Why is peer review important?
Peer review is vitally important to uphold the high standards of scholarly communications, and maintain the quality of individual journals. It is also an important support for the researchers who author the papers.
Every journal depends on the hard work of reviewers who are the ones at the forefront of the peer review process. The reviewers are the ones who test and refine each article before publication. Even for very specialist journals, the editor can’t be an expert in the topic of every article submitted. So, the feedback and comments of carefully selected reviewers are an essential guide to inform the editor’s decision on a research paper.
There are also practical reasons why peer review is beneficial to you, the author. The peer review process can alert you to any errors in your work, or gaps in the literature you may have overlooked.
Researchers consistently tell us that their final published article is better than the version they submitted before peer review. 91% of respondents to a Sense about Science peer review survey said that their last paper was improved through peer review. A Taylor & Francis study supports this, finding that most researchers, across all subject areas, rated the contribution of peer review towards improving their article as 8 or above out of 10.
Choose the right journal for your research: Think. Check. Submit
We support Think. Check. Submit., an initiative launched by a coalition of scholarly communications organizations. It provides the tools to help you choose the right journal for your work.
Think. Check. Submit. was established because there are some journals which do not provide the quality assurance and services that should be delivered by a reputable journal. In particular, many of these journals do not make sure there is thorough peer review or editor feedback process in place.
That means, if you submit to one of these journals, you will not benefit from helpful article feedback from your peers. It may also lead to others being skeptical about the validity of your published results.
You should therefore make sure that you submit your work to a journal you can trust. By using the checklist provided on the Think. Check. Submit. website, you can make an informed choice.
Peer review integrity at Taylor & Francis

Every full research article published in a Taylor & Francis journal has been through peer review, as outlined in the journal’s aims & scope information. This means that the article’s quality, validity, and relevance has been assessed by independent peers within the research field.
We believe in the integrity of peer review with every journal we publish, ascribing to the following statement:
All published research articles in this journal have undergone rigorous peer review, based on initial editor screening, anonymous refereeing by independent expert referees, and consequent revision by article authors when required.
Peer review takes different forms and each type has pros and cons. The type of peer review model used will often vary between journals, even of the same publisher. So, check your chosen journal’s peer-review policy before you submit, to make sure you know what to expect and are comfortable with your paper being reviewed in that way.
Every Taylor & Francis journal publishes a statement describing the type of peer review used by the journal within the aims & scope section on Taylor & Francis Online.
Below we go through the most common types of peer review.
Common types of peer review
Single-anonymous peer review
This type of peer review is also called ‘single-blind review’. In this model, the reviewers know that you are the author of the article, but you don’t know the identities of the reviewers.
Single-anonymous review is most common for science and medicine journals.
Find out more about the pros and cons of single-anonymous peer review.
Double-anonymous peer review
In this model, which is also known as ‘double-blind review’, the reviewers don’t know that you are the author of the article. And you don’t know who the reviewers are either. Double-anonymous review is particularly common in humanities and some social sciences’ journals.
Discover more about the pros and cons of double-anonymous peer review.
If you are submitting your article for double-anonymous peer review, make sure you know how to make your article anonymous.
Open peer review
There is no one agreed definition of open peer review. In fact, a recent study identified 122 different definitions of the term. Typically, it will mean that the reviewers know you are the author and also that their identity will be revealed to you at some point during the review or publication process.
Find out more about open peer review.
Post-publication peer review
In post-publication peer review models, your paper may still go through one of the other types of peer review first. Alternatively, your paper may be published online almost immediately, after some basic checks. Either way, once it is published, there will then be an opportunity for invited reviewers (or even readers) to add their own comments or reviews.
You can learn about the pros and cons of post-publication peer review here.
Registered Reports
The Registered Reports process splits peer review into two parts.
The first round of peer review takes place after you’ve designed your study, but before you’ve collected or analyzed any data. This allows you to get feedback on both the question you’re looking to answer, and the experiment you’ve designed to test it.
If your manuscript passes peer review, the journal will give you an in-principle acceptance (IPA). This indicates that your article will be published as long as you successfully complete your study according to the pre-registered methods and submit an evidence-based interpretation of the results.
F1000Research is part of the Taylor & Francis Group. It operates an innovative peer review process which is fully transparent and takes place after an article has been published.
How it works
Before publication, authors are asked to suggest at least five potential reviewers who are experts in the field. The reviewers also need to be able to provide unbiased reports on the article.
Submitted articles are published rapidly, after passing a series of pre-publication checks that assess, originality, readability, author eligibility, and compliance with F1000Research’s policies and ethical guidelines.
Once the article is published, expert reviewers are formally invited to review.
The peer review process is entirely open and transparent. Each peer review report, plus the approval status selected by the reviewer, is published with the reviewer’s name and affiliation alongside the article.
Authors are encouraged to respond openly to the peer review reports and can publish revised versions of their article if they wish. New versions are clearly linked and easily navigable, so that readers and reviewers can quickly find the latest version of an article.
The article remains published regardless of the reviewers’ reports. Articles that pass peer review are indexed in Scopus, PubMed, Google Scholar and other bibliographic databases.
How our publishing process works for articles
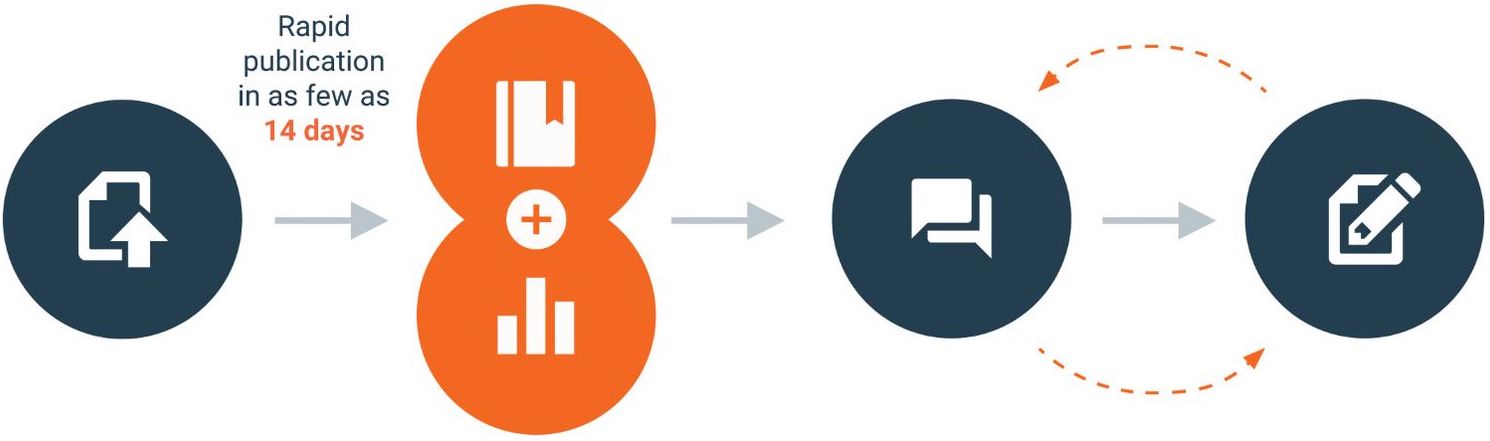
1. Article submission
Submitting an article is easy with our single-page submission system.
The in-house editorial team carries out a basic check on each submission to ensure that all policies are adhered to.
2. Publication and data deposition
Once the authors have analysed the manuscript, the article (with its associated source data) is published within a week, enabling immediate viewing and caution.
3. Open peer review & user commenting
Expert reviewers are selected and invited. Their reports and names are published alongside the article, together with the authors’ responses and comments from registered users.
4. Article revision
Authors are encouraged to publish revised versions of their article. All versions of an article are linked and independently citable.
Articles that pass peer review are indexed in external databases such as PubMed, Scopus and Google Scholar.
Discover more about how the F1000Research model works.
Peer review follows a number of steps, beginning with submitting your article to a journal.
Step 1: Editor assessment
When your manuscript arrives at the journal’s editorial office it will receive an initial desk assessment by the journal’s editor or editorial office. They will check that it’s broadly suitable for the journal.
They will ask questions such as:
Is this the right journal for this article?
Does the paper cover a suitable topic according to the journal’s aims & scope?
Has the author followed the journal’s guidelines in the instructions for authors? They will check that your paper meets the basic requirements of the journal, such as word count, language clarity, and format.
Has the author included everything that’s needed for peer review? They will check that there is an abstract, author affiliation details, any figures, and research-funder information.
Does it make a significant contribution to the existing literature?


If your article doesn’t pass these initial checks the editor might reject the article immediately. This is known as a ‘desk reject’ and it is a decision made at the editor’s discretion, based on their substantial experience and subject expertise. By having this initial screening in place, it can enable a quick decision if your manuscript isn’t suitable for the journal. This means you can submit your article to another journal quickly.
If your article does pass the initial assessment, it will move to the next stage, and into peer review.
“As an editor, when you first get a submission, at one level you’re simply filtering. A fairly small proportion do not get sent out by me for review. Sometimes they simply fall outside the scope of the journal.”
– Michael Reiss, Founding Editor of Sex Education
Step 2: First round of peer review
Next, the editor will find and contact other researchers who are experts in your field, and will ask them to review the paper. A minimum of two independent reviewers is normally required for every research article. The aims and scope of each journal will outline their peer review policy in detail.
The reviewers will be asked to read and comment on your article. They may also be invited to advise the editor whether your article is suitable for publication in that journal.
So, what are the reviewers looking for?
This depends on the subject area, but they will be checking that:
Your work is original or new.
The study design and methodology are appropriate and described so that others could replicate what you have done.
You’ve engaged with all the relevant current scholarship.
The results are appropriately and clearly presented.
Your conclusions are reliable, significant, and supported by the research.
The paper fits the scope of the journal.
The work is of a high enough standard to be published in the journal.
IMPORTANT
If you have not already shared your research data publicly, peer reviewers may request to see your datasets, to support validation of the results in your article.
Once the editor has received and considered the reviewer reports, as well as making their own assessment of your work, they will let you know their decision. The reviewer reports will be shared with you, along with any additional guidance from the editor.
If you get a straight acceptance, congratulations, your article is ready to move to publication. But, please note, that this isn’t common. Very often, you will need to revise your article and resubmit it. Or it may be that the editor decides your paper needs to be rejected by that journal.
Please note that the final editorial decision on a paper and the choice of who to invite to review is always the editor’s decision. For further details on this, please see our peer review appeals and complaints policy.

Step 3: Revise and resubmit
It is very common for the editor and reviewers to have suggestions about how you can improve your paper before it is ready to be published. They might have only a few straightforward recommendations (‘minor amendments’) or require more substantial changes before your paper will be accepted for publication (‘major amendments’). Authors often tell us that the reviewers’ comments can be extremely helpful, to make sure that their article is of a high quality.
During this stage of the process you will have time to amend your article based on the reviewers’ comments, resubmitting it with any or all changes made. Make sure you know how to respond to reviewer comments, we cover this in the next section.
Once you resubmit your manuscript the editor will look through the revisions. They will often send it out for a second round of peer review, asking the reviewers to assess how you’ve responded to their comments.
After this, you may be asked to make further revisions, or the paper might be rejected if the editor thinks that the changes you’ve made are not adequate. However, if your revisions have now brought the paper up to the standard required by that journal, it then moves to the next stage.
If you do not intend to make the revisions suggested by the journal and resubmit your paper for consideration, please make sure you formally withdraw your paper from consideration by the journal before you submit elsewhere.
Make sure you resubmit
If you have not already shared your research data publicly, peer reviewers may request to see your datasets to support the validation of the results in your article.
Step 4: Accepted
And that’s it, you’ve made it through peer review. The next step is production
How long does peer review take?
Editorial teams work very hard to progress papers through peer review as quickly as possible. But it is important to be aware that this part of the process can take time.
The first stage is for the editor to find suitably qualified expert reviewers who are available. Given the competing demands of research life, nobody can agree to every review request they receive. It’s therefore not uncommon for a paper to go through several cycles of requests before the editor finds reviewers who are both willing and able to accept.
Then, the reviewers who do accept the request, have to find time alongside their own research, teaching, and writing, to give your paper thorough consideration.
Please do keep this in mind if you don’t receive a decision on your paper as quickly as you would like. If you’ve submitted your paper via an online system, you can use it to track the progress of your paper through peer review. Otherwise, if you need an update on the status of your paper, please get in touch with the editor.
Top tip
Many journals publish key dates alongside new articles, including when the paper was submitted, accepted, and published online. While you’re at the stage of choosing a journal to submit to, take a look at these dates for a range of recent articles published in the journals you’re considering. While each article will have a slightly different timeline, this may help you to get an idea of how long publication may take.
A 360⁰ view of peer review
Peer review is a process that involves various players – the author, the reviewer and the editor to name a few. And depending on which of these hats you have on, the process can look quite different.
To help you uncover the 360⁰ peer review view, read these interviews with an editor, author, and reviewer.

If the editor asks you to revise your article, you will be given time to make the required changes before resubmitting.

When you receive the reviewers’ comments, try not to take personal offence to any criticism of your article (even though that can be hard).
Some researchers find it helpful to put the reviewer report to one side for a few days after they’ve read it for the first time. Once you have had chance to digest the idea that your article requires further work, you can more easily address the reviewer comments objectively.
When you come back to the reviewer report, take time to read through the editor and reviewers’ advice carefully, deciding what changes you will make to your article in response. Taking their points on board will make sure your final article is as robust and impactful as possible.
Please make sure that you address all the reviewer and editor comments in your revisions.
It may be helpful to resubmit your article along with a two-column grid outlining how you’ve revised your manuscript. On one side of the grid list each of the reviewers’ comments and opposite them detail the alterations you’ve made in response. This method can help you to order your thoughts, and clearly demonstrate to the editor and reviewers that you’ve considered all of their feedback.
If there are any review comments which you don’t understand or don’t know how to respond to, please get in touch with the journal’s editor and ask for their advice.
What if you don’t agree with the reviewers’ comments?
If there’s a review comment that you don’t agree with, it is important that you don’t ignore it. Instead, include an explanation of why you haven’t made that change with your resubmission. The editor can then make an assessment and include your explanation when the amended article is sent back to the reviewers.
You are entitled to defend your position but, when you do, make sure that the tone of your explanation is assertive and persuasive, rather than defensive or aggressive.
“Where possible, a little constructive advice on how to make use of the views of the referees can make all the difference, and the editor has the responsibility of deciding when and how to do this.”
– Gary McCulloch, Editor, British Journal of Educational Studies
Nobody enjoys having their paper rejected by a journal, but it is a fact of academic life. It happens to almost all researchers at some point in their career. So, it is important not to let the experience knock you back. Instead, try to use it as a valuable learning opportunity.
Take time to understand why your paper has been rejected
If a journal rejects your manuscript, it may be for one of many reasons. Make sure that you understand why your paper has been rejected so that you can learn from the experience. This is especially important if you are intending to submit the same article to a different journal.
Are there fundamental changes that need to be made before the paper is ready to be published, or was this simply a case of submitting to the wrong journal? If you are unsure why your article has been rejected, then please contact the journal’s editor for advice.

Some of the common reasons manuscripts are rejected
The author has submitted their paper to the wrong journal: it doesn’t fit the aims & scope or fails to engage with issues addressed by the journal.
The manuscript is not a true journal article, for instance it is too journalistic or clearly a thesis chapter.
The manuscript is too long or too short.
There is poor regard of the journal’s conventions, or for academic writing in general.
Poor style, grammar, punctuation or English throughout the manuscript. Get English language editing assistance.
The manuscript does not make any new contribution to the subject.
The research has not been properly contextualized.
There is a poor theoretical framework used. There are actionable recommendations to improve your manuscript.
The manuscript is poorly presented.
The manuscript is libelous or unethical.
Carefully consider where to submit next
When you made your original submission, you will probably have had a shortlist of journals you were considering. Return to that list but, before you move to your second choice, you may wish to assess whether any feedback you’ve received during peer review has changed your opinion. Your article may also be quite different if it has been through any rounds of revision. It can be helpful at this stage to re-read the aims & scope statements of your original shortlisted journals.
Once you have selected which journal to submit to next, make sure that you read through its information for authors and reformat your article to fit its requirements. Again, it is important to use the feedback from the peer review process to your advantage as you rewrite and reformat the manuscript.
Is ‘transferring’ an option?
A growing number of publishers offer a transfer or cascade service to authors when their paper is rejected. This process is designed for papers which aren’t suitable for the journal they were originally submitted to.
If your article falls into this category then one or more alternative journals from the same publisher will be suggested. You will have the option either to submit to one of those suggested journals for review or to withdraw your article.
If you choose to transfer your article this will usually save you time. You won’t need to enter all of the details into a new submission system. Once you’ve made any changes to your paper, bearing in mind previous editor or reviewer comments, the article will be submitted to the new journal on your behalf.
We have some more information about article transfers, and also some FAQs about the Taylor & Francis transfer process.
When you’re not in the middle of submitting or revising your own article, you should consider becoming a reviewer yourself.
There are many demands on a researcher’s time, so it is a legitimate question to ask why some of that precious time should be spent reviewing someone else’s work. How does being a reviewer help you in your career? Here are some of the benefits.
Keep up with the latest thinking
As a reviewer you get an early view of the exciting new research being done in your field. Not only that, peer review gives you a role in helping to evaluate and improve this new work.Improve your own writing
Carefully reviewing articles written by other researchers can give you an insight into how you can make your own work better. Unlike when you are reading articles as part of your research, the process of reviewing encourages you to think critically about what makes an article good (or not so good). This could be related to writing style, presentation, or the clarity of explanations.
Boost your career
While a lot of reviewing is anonymous, there are schemes to recognize the important contribution of reviewers. You can also include reviewing work on your resume. Your work as a reviewer will be of interest to appointment or promotion committees who are looking for evidence of service to the profession.Become part of a journal’s community
Many journals act as the center of a network of researchers who are in conversation about key themes and developments in the field. Becoming a reviewer is a great way to get involved with that group. This can give you the opportunity to build new connections for future collaborations. Being a regular reviewer may also be the first step to becoming a member of the journal’s editorial board.
Your research community needs you
Of course, being a reviewer is not just about the benefits it can bring you. The Taylor & Francis peer review survey found that these are the top 3 reasons why researchers choose to review:
Being an active member of the academic community
Peer review is the bedrock of academic publishing. The work of reviewers is essential in helping every piece of research to become as good as it can be. By being a reviewer, you will play a vital part in advancing the research area that you care about.Reciprocating the benefit
Researchers regularly talk about the benefits to their own work from being reviewed by others. Gratitude to the reviewers who have improved your work is a great motivation to make one’s own contribution of service to the community.Enjoying being able to help improve papers
Reviewing is often anonymous, with only the editor knowing the important contribution you’ve made. However, many reviewers attest that it is work that makes them feel good, knowing that they have been able to support a fellow researcher.
How to be an effective peer reviewer
Our popular guide to becoming a peer reviewer covers everything you need to know to get started, including:
How to become a peer reviewer
Writing review reports: step-by-step
Ethical guidelines for peer reviewers
Reviewer recognition
Read the Taylor & Francis reviewer guidelines.
“Reviewers are the lifeblood of any journal”
– Mike J. Smith, Editor-in-Chief of Journal of Maps
We hope you’ve found this short introduction to peer review helpful. For further useful advice check out the following resources.
Further resources
Peer Review: the nuts and bolts
A guide to peer review written by early career researchers, for early career researchers and published by Sense about Science.A guide to becoming a peer reviewer
An overview of what’s involved in becoming a reviewer for a Taylor & Francis journal.Ethical guidelines for peer reviewer
Produced by COPE, the Committee on Publication Ethics, setting out the standards all peer reviewers should follow.Using peer review effectively: quick tips
Advice available to staff and students at institutions with a Vitae membership.
Publishing tips, direct to your inbox
Expert tips and guidance on getting published and maximizing the impact of your research. Register now for weekly insights direct to your inbox.



